Research Paper - https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.02799
Authors - Jacob Andreas, Marcus Rohrbach, Trevor Darrell, Dan Klein ## Key Idea Parse questions of visual QA into a description of compositions of functions. These functions are neural networks called Neural Modules. Execute the neural networks and reweigh the resulting label using question representation. 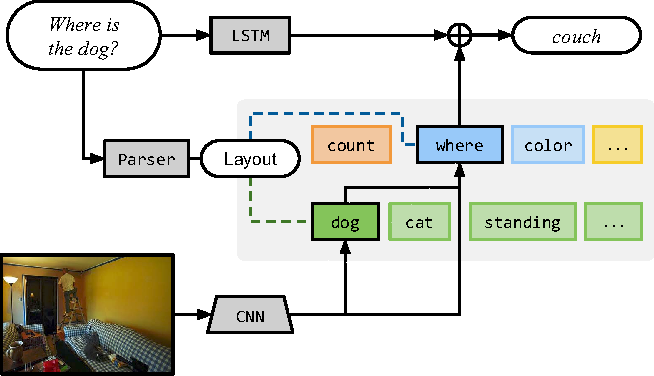 ## Task - Visual Question Answering Given a question like “What color is the coffee mug?” and an image we want to predict the answer.
## Task - Visual Question Answering Given a question like “What color is the coffee mug?” and an image we want to predict the answer.  ## Prior approaches
## Prior approaches
End to End neural networks
Use a CNN to vectorize the image and RNN to vectorize the question and use a feed forward network to classify the answer. This is a black box trying to answer in one shot.
Semantic Parsing approach
Parse the question into logical expressions, image into logical representation of the world and use logic based reasoning to solve the problem. This is more compositional. ## Motivation Combine the representational capacity of neural nets and compositionality of symbolic approach.
“Rather than thinking of question answering as a problem of learning a single function to map from questions and contexts to answers, it’s perhaps useful to think of it as a highly-multitask learning setting, where each problem instance is associated with a novel task, and the identity of that task is expressed only noisily in language.”
Simple example - “Is this a truck?” - Needs single task to be performed, namely truck or not classification.
Compositional example - “What is the object to the left of the tea pot?” - Needs one to find the teapot, detect object to its left, then classify the object. ## Architecture ### Neural Modules Identify set of modules that can be composed to solve all/most tasks. Modules can be thought of as a function parametrized by a neural network, with a type signature. Data Types - Image, Unnormalized attention map, labels 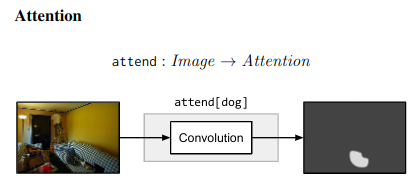
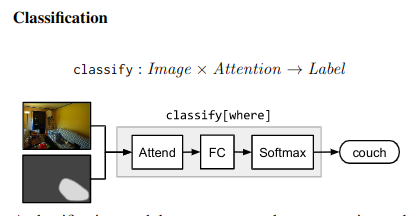
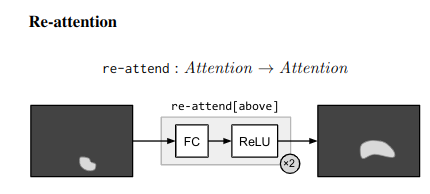
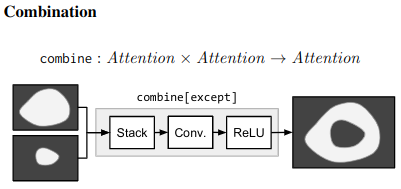
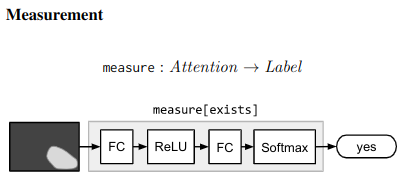 ### Strings -> Modules Parsing Use few rules on dependency parse of the question to convert it into a structured query. e.g. “Is there a circle next to a square?” -> is(circle, next-to(square)) Layout “All leaves become attend modules, all internal nodes become re-attend or combine modules dependent on their arity, and root nodes become measure modules for yes/no questions and classify modules for all other question types.” The queries could come from anywhere not just natural language question. As long as they can be converted to a layout in the end. ### Answering An RNN is used to process the question and predict a label directly without looking into the image. This is combined with the final label from the root node of the Neural Modules using geometric mean to get the final result. This is done for 2 reasons Syntactic Regularity/Prior When converting to structured query, certain syntactic elements are lost. For e.g. What is in the sky? and What are in the sky? both result in what(fly). But answer varies from kite to kites. Semantic Regularity/Prior Some answers are unreasonable just by inspecting the question. For example, What colour is the bear? eliminates all non-colour answers. ## Benchmarks They try this in vqa dataset - https://visualqa.org/ a huge dataset with natural images and questions with answers.
### Strings -> Modules Parsing Use few rules on dependency parse of the question to convert it into a structured query. e.g. “Is there a circle next to a square?” -> is(circle, next-to(square)) Layout “All leaves become attend modules, all internal nodes become re-attend or combine modules dependent on their arity, and root nodes become measure modules for yes/no questions and classify modules for all other question types.” The queries could come from anywhere not just natural language question. As long as they can be converted to a layout in the end. ### Answering An RNN is used to process the question and predict a label directly without looking into the image. This is combined with the final label from the root node of the Neural Modules using geometric mean to get the final result. This is done for 2 reasons Syntactic Regularity/Prior When converting to structured query, certain syntactic elements are lost. For e.g. What is in the sky? and What are in the sky? both result in what(fly). But answer varies from kite to kites. Semantic Regularity/Prior Some answers are unreasonable just by inspecting the question. For example, What colour is the bear? eliminates all non-colour answers. ## Benchmarks They try this in vqa dataset - https://visualqa.org/ a huge dataset with natural images and questions with answers.  Since VQA doesn’t have many deep compositional questions, they use shapes a synthetically generated dataset.
Since VQA doesn’t have many deep compositional questions, they use shapes a synthetically generated dataset.  ## Examples What colour is his tie?
## Examples What colour is his tie? 
